First we need to install redis.
System Preference: Ubuntu 16.04
[We have created VM on www.digitalocean.com]
Execute Following:
sudo apt-get install make sudo apt-get install git sudo apt-get update sudo apt-add-repository ppa:chris-lea/redis-server sudo apt-get install build-essential tcl
Download and Install Redis
wget http://download.redis.io/releases/redis-5.0.5.tar.gz tar xzf redis-5.0.5.tar.gz cd redis-5.0.5 make sudo make install
If you want to run Redis Server with default Configuration
/redis-5.0.5/src/redis-server
Move Configuration file to /etc/redis/redis.conf
sudo mkdir /etc/redis sudo cp /redis-5.0.5/redis.conf /etc/redis
Find the dir directory. This option specifies the directory that Redis will use to dump persistent data. We need to pick a location that Redis will have write permission and that isn’t viewable by normal users.We will use the /var/lib/redis directory for this, which we will create in a moment.
sudo nano /etc/redis/redis.conf In Dir sudo mkdir /var/lib/redis
Now, we want to setup a cluster environment like following:
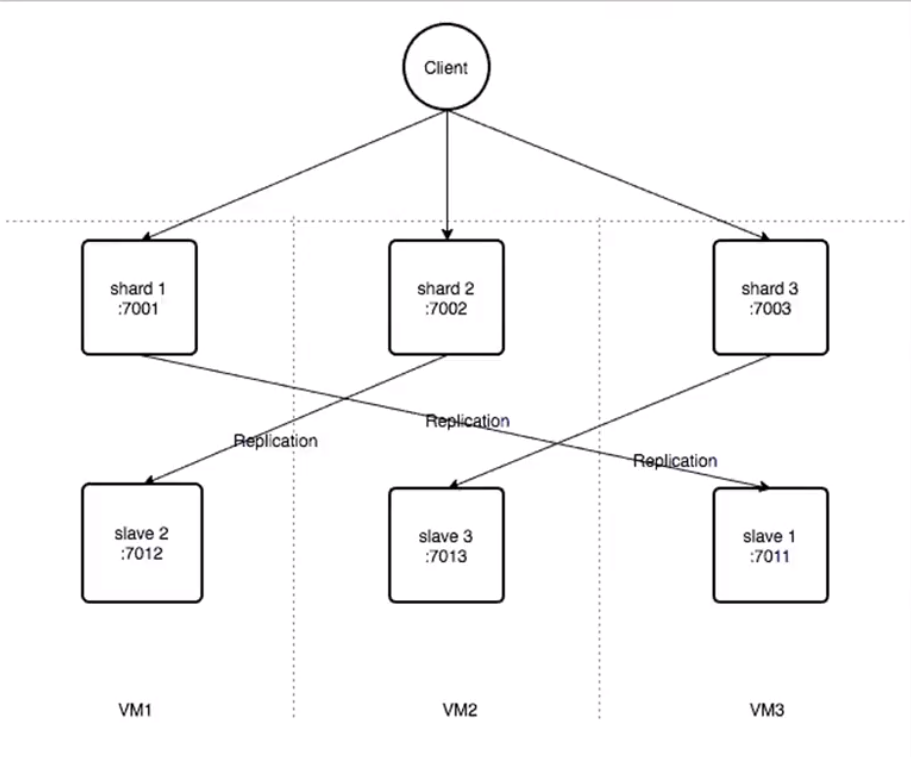
For this we have to go through few steps more. Need to produce configuration file for each Node. We can clone that from git repo.
git clone https://github.com/arifmarias/redisconfig.git
Copy those to /etc/redis directory. Each of the conf file has got following with slight changes. Like inside Node1.conf file we have following:
port 7001 cluster-enabled yes cluster-config-file cluster-node-1.conf cluster-node-timeout 5000 appendonly yes appendfilename node-1.aof dbfilename dump-1.rdb bind 127.0.0.1 bind 0.0.0.0 protected-mode yes
So, now if you want to run Redis servers (6 of them) then need to execute following line for each separate Node:
./redis-5.0.5/src/redis-server /etc/redis/node1.conf
Now its time to deploy our cluster by executing following command:
./src/redis-cli --cluster create 127.0.0.1:7001 127.0.0.1:7002 127.0.0.1:7003 127.0.0.1:7004 127.0.0.1:7005 127.0.0.1:7006 --cluster-replicas 1
For further FAQ you can visit this blog ( why we need to create 6 Nodes ( 3 Primary and 3 Slaves): https://serverfault.com/questions/815764/redis-cluster-3-master-nodes-minimum
Now, if i want to run my cluster from any of the master node:
./src/redis-cli -c -p 7001
You can execute some Redis command if you like and see how cluster is managing your data persistently.
SET x 1 SET y 2 SET z 3 keys * get y keys *
You can force kill Node 2 ( which running on 7002) then you will see how master slave changes.
[It will wait a few second then slave node promoted to master node] keys* get z Moved to 7005 [Then restart the service to Node 2. It will rejoin the cluster but Node 2 will be slave of Node 5.] [Kill Node 5 Then Node 2 become master again.] Get z (Redirect to 7002)
If you’re not sure whether the Redis instance you’re currently connected to is a primary instance or a replica, you can check by running the role command:
role
To designate a Redis instance as a replica of another instance on the fly, run the replicaof command. This command takes the intended primary server’s hostname or IP address and port as arguments:
replicaof hostname_or_IP port
If the server was already a replica of another primary, it will stop replicating the old server and immediately start synchronizing with the new one. It will also discard the old dataset.
To promote a replica back to being a primary, run the following replicaof command:
replicaof no one
This will stop the instance from replicating the primary server, but will not discard the dataset it has already replicated. This syntax is useful in cases where the original primary fails. After running replicaof no one on a replica of the failed primary, the former replica can be used as the new primary and have its own replicas as a failsafe.